Dear Dr Paul,
Please review case study and advice better approach carrying out this comparison and analysis. Excerpts from AACE forums/discussions website: http://www.aacei.org/cgi-bin/forums/discus.cgi
1. Problem recognition, definition and evaluation
Good Project Management involves successful completion of the project in time within budget and without compromising on quality. In recent years, technological innovation, use of computer applications with the internet in construction projects has significantly enhanced fulfilling aforementioned project objective. Hence this week’s case study is to quantify the project management efficiency (PME) using computer applications as compared to traditional project management system.
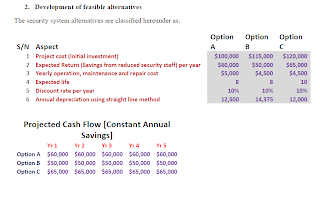
2. Development of the feasible alternatives
There are two main types of project management systems:
1. Traditional Project management system - The traditional project management system uses orthodox methods and techniques, linear and incremental management processes. These methods and techniques have been evolved for decades and are applicable for most of the domains. But for some domains, such as software development, traditional project management is not a 100% fit.
2. Modern Project management system - Therefore, there have been a few modern project management practices, interactive and adaptive, introduced to address the shortcomings of the traditional method. Below are five such modern project management applications:
1. Microsoft Project - Microsoft Project is one of the more popular packages and it now offers a web interface and deep Office, Outlook and SharePoint integration.
2. Matchware MindView - MindView has an easy-to-use spreadsheet-like layout, and its mind map option lets you see your project in visuals, reminiscent of brainstorming bubbles.
3. Project Kickstart - Project KickStart is an easy-to-use project management package that integrates with other applications like PowerPoint, Outlook, Excel, Word, Microsoft Project, and ACT!.
4. RationalPlan Multi Project - RationalPlan Multi Project has features to manage resources and budgets as well as multiple projects. It has an interactive Gantt chart, normally available only in higher-end suites.
5. Basecamp - Basecamp is a low-cost web-based project management and collaboration package which is gaining momentum.
3. Development of the outcomes and cash flows for each alternative
4. Selection of the acceptable criteria
In today's world, project management methods need to be flexible enough to enable handling and management of multiple changes simultaneously, using modern computer applications based on selected criteria such as efficiency, compatibility, speed, accuracy, accessibility and flexibility for switching between applications.
5. Analysis and Comparison of the alternatives
Contemporary project management, interactive and adaptive process stresses more on the EXECUTION (EV), rather than the PLANNING (PV) aspect of a project. This does not mean that planning is not important, but the key stress and the main focus should be on the EXECUTION (EV) aspect of the project once the project has exited envisioning and planning phases.
6. Selection of the preferred alternative
The evaluation of PME with the use of modern computer applications, tools and techniques can serve for project managers and project organizations as indicator for measuring level of achievements of project management objectives and project teams performance evaluation.
7. Performance Monitoring and Post Evaluation of Results
We are now transitioning to a new arena where project management skills have increasingly being called out as 'essential' in an organization due to the increased complexities in today's projects and the multiple problems around and thereby replacing predictive planning with adaptive planning methodologies, using modern computer applications, tools and techniques.
8. References/Bibliography
1. AACE forums/discussions website:
2. Effective Project Management: Traditional, Agile, Extreme: http://www.amazon.com/Effective-Project-Management-Traditional-Extreme/dp/0470423676
www.aacei.org › Professional Resources
http://www.aacei.org/resources/rp/