Problem definition
Cost Estimating Methods
Cost estimating is the predictive process used to
quantify, cost and price the resources required by the scope of investment
option, activity or project. Depending on the stage of the project, three main
methods are used to estimate costs. What are the features of the cost
estimating methods?
Feasible alternatives
Engineering build up method
Analogy method
Parametric method
Develop the outcome of each
alternative
1 Analogy
The analogy
uses actual costs from a similar program with adjustments to account for
differences between the requirement of the existing and the new one.
2 Engineering Build-Up Method
The
engineering build-up method sometimes called bottom-up method uses the WBS to
build costs from the lowest level of details and summing up to get the overall
cost. Because of the high level of detail each step of the work flow should be
identified, measured, and tracked and the result for each outcome should be
summed to make the estimate.
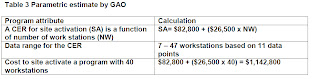
3 Parametric Method
A parametric model
is a mathematical representation of of cost relationships that provide a
logical and predictable correlation between the physical or functional
characteristics of a plant (or process system) and its resultant cost. It
relies on collection and analysis of data from previous projects to arrive at a
cost estimating relationship (CER)
The attribute for the selection criteria is;
·
Strength
·
Weakness
·
Application
Analysis of alternatives
Selection of preferred alternative
The estimate development process is a logical one. The
method to be adopted depends on the amount of available detail for project
scope. Engineering Build-up method is
employed for detailed or definitive type estimate, because it relies on the
availability of detailed design and scope information. The Analogy and
Parametric Methods are used for conceptual estimates because they do not
require detailed information. Any or all of the three methods can be used in
the preliminary estimate depending on the amount of specific information that
is available.
Performance monitoring and evaluation
An estimate
is a prediction of the expected final cost of a proposed project and is
therefore associated with uncertainty and probability of underruning or
overrunning the predicted cost. This uncertainty necessitates the need for
validation of the estimate by looking for errors and cross-checks on various
cost drivers. Equally independent cost estimate should be compared with the
predicted estimate and the difference reconciled.
References
Dysert, L. R. Estimating, Skills & Knowledge of Cost
Engineering (5th ed.), (PP 9.1.-9.34) WV, AACE International
Developing a Point Estimate, GAO Cost Estimating and
Assessment Guide (February 2005.), (PP. 107-123) Washington, DC, retrieved from
http://www.gao.gov/cgi-bin/getrpt?GAO-05-325SP .
Humphreys, G. C. (2011). Estimate Development, Project
Management Using Earned Value (2nd ed.), (PP. 401-417) CA, Humphreys
& Associates Inc.
Project Management Estimating Tools & Techniques,
Project Management Guide retrieved from http://www.projectmanagementguru.com/estimating.html.
Giammalvo P.
D. Activity Based Cost Management, AACE Certification Preparatory Course-Day 5



Hmmmmmm........ Not bad, Charles, but you missed quite a few methods......
ReplyDeleteGo to my handouts from Day 2, slides 75-84. What about target costing? End Unit Costing? Indices? Gold Equivalency?
I will accept this posting but I expect you go create another blog posting which includes ALL the different methods, not just the three you identified.....
You also need to be clear what class of estimate each is good for....
BR,
Dr. PDG, Jakarta