W12_LUCKY_COMPARING EARNED VALUE MEASUREMENT METHODS
1. Problem Recognition, Definition, Root Cause Analysis and Evaluation
a. Problem Recognition
The earned value of any particular deliverable is defined as the planned value multiplied by the percentage complete. However, one of the most difficult areas of earned value management is the determination of the earned value or budgeted cost of work performed.
b. Problem Definition
The percentage complete is calculated by using a predetermined earned value measurement method. Given the fact that there are several earned value measurement methods in existence, what would comparing these earned value measurement methods reveal regarding proper reflection of the progress of work?
c. Root Cause Analysis and Evaluation
Determining an appropriate earned value measurement method or technique for some projects of Team Bistro 12 has been challenging for a majority of the team members. This could be due to a lack of proper understanding of the application of the various earned value techniques.
2. Development of Feasible Alternatives
For the purpose of determining the budgeted cost of work performed (BCWS), work tasks are classified broadly into the following three types[i]:
1. Discrete Effort
o Used for physical, tangible end product[ii] (See further examples below)
2. Apportioned Effort
o Used for discrete work effort, but dependent on another discrete work package (e.g. quality assurance)
3. Level of Effort(LOE)
o No tangible end product
o Time is the basis of measurement (e.g. project management personnel)
Discrete Effort methods that have been extensively used over the years include:
1. Incremental Milestones[iii]
2. 50/50 Method
3. 0/100 Method
4. Equivalent Units
5. Units Complete
6. Percent Complete
7. Combination of the above
The above classification of work measurement types constitute the alternatives of the earned value technique from which a selection can be made.
3. Development of outcomes for each alternative
Focusing on the discrete work measurement techniques, value is earned as follows:
Method How Value is earned
0/100 No earned value at start, 100% at close of work package
50/50 50% at start, 50% at close of work package
Units completed same budget value for identical units (physical count of products)
Equivalent units planned units' standards allowing for partial credits
Weighted milestones each milestone weighted based on planned resources
Percent complete subjective
4. Selection Criteria
The selection criterion is: Accuracy of work progress monitoring
5. Analysis and Comparison of the alternatives
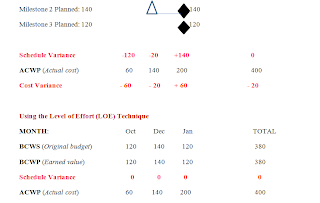
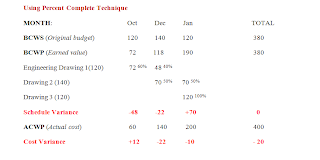
MONTH: Oct Dec Jan TOTAL
Milestone SV -120 -20 +140 0
CV - 60 - 20 + 60 - 20
LOE SV 0 0 0 0
CV +60 0 -80 - 20
50/50 SV 0 -190 +190 0
CV +130 -140 -10 - 20
% Complete SV -48 -22 +70 0
CV +12 -22 -10 - 20
6. Selection of preferred alternative
Of the earned value techniques presented in this write up– milestone, LOE, 50/50, and % complete – the milestone method provided the most accurate representation of the work progress during the period. Besides, trending both the Schedule variance and Cost variance, there were improvements over the period.
7. Performance monitoring and post evaluation of results
For the purpose of performance monitoring, it would be good to use different EVM measurement methods for different milestones within the same project. However, I would use EVM method that gives the most accurate result for each milestone. Better still, I would advise my management to establish a standard set of project activities with the preferred measurement methods to ensure consistency in receiving credit for work completed.
Reference
[i] Humphreys, G. (2002). Chapter 31 Measuring Accomplishment (pp. 621 -633). Project management using earned value (1st edition). Orange CA.: Humphreys & Associates, Inc.
[ii] Haupt, E. & Carter, L. (2000). CPM 300 Principles of earned value implementation: CPM 300B – Management use of EV data. Retrieved from http://www.evmlibrary.org/library/CPM-300B%20Interpreting%20EVM%20Data,%20Haupt%20&%20Carter(2).pdf
[iii] Giammalvo, P. (2012, October 22). Integrated portfolio (asset), program (operations) and project management methodology course (cost engineering) Day 5 slides 50 -51 (An AACE methodology course). Lagos, Nigeria: Lonadek



AWESOME, Lucky!!!
ReplyDeleteI provided you with the method to measure the Blog Posting progress (units in place method) and the paper (incremental milestone method.
My challenge to each of you is how do you want to measure the REMAINING projects?
Weekly Report?
Mapping Project?
Questions Project?
Mid Term Exam?
What method of EVM is best suited to accurately measure % progress on each of these projects?
Keep up the great work, Lucky!!!
BR,
Dr. PDG, Jakarta